Merchant Account Glossary of Terms
There are a variety of terms used in the merchant account business and
sometimes not knowing these terms can make it difficult to know if you
are getting a good deal or not. We feel our job is to educate you and
for us, an educated customer, is our best customer. Below are the
definitions for most common merchant account terms.
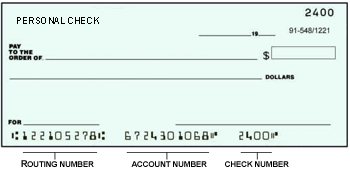
- ABA Routing Number: This is the nine digit
American Bankers Association number sometimes referred to instead as
only the Routing number or
alternatively as the Transit Routing Number that appears at the bottom
of your check next to your checking account number and the individual
check number. Each back has its on ABA Routing number so it uniquely
references a bank and so in a sense is the Banks account number. On a
business checking typically the check number appears first before the
Routing Number compared to a personal check where it appears first.

- ACH stands for Automated Clearing House. This is
the alternative technique to accept payments from credit card acceptance
that is typically used or associated in what is called "Electronic
Checks". An ACH is a payment from one bank account to another. ACH
payments, like checks are not guaranteed and can bounce like checks
until they finish a process called "settlement". ACH Settlement is the
time and process by which these electronic payments are followed by
paper process via the Federal Reserve to confirm they are authentic.
- Acquiring Bank. This is the merchant account bank
that has the direct relationship with Visa and MasterCard. The
acquiring bank performs the deposits and recovery of funds and fees
between the cardholders bank or issuing bank and your merchant checking
account.
- Authorization. This is the process ONLY of
Validating funds are available at the issuing bank for the individual
cardholder. It is the first step of processing a credit card. An
authorization in and of itself does cause a funds transfer but rather
"earmarks" those funds as "transacted" on behalf of the acquiring bank.
This occurs in real time and a six or seven digit authorization number
or code is issued indicating the authorization was accepted. If the
code is not returned, a decline is returned instead.
- Authorization Code. The six or seven digit number
provided by the terminal that indicates an authorization has been
approved and accepted. Its important for the merchant to keep track of
this number as it serves as proof of authorization.
- Auth Only or Authorization Only Transaction.
A type of transaction where the sale is Authorized only but the funds
are not captured and the funds are not settled. This is useful to
earmark funds for a purchase until such a time that the goods and
services are delivered or the actual charges are determined. Its
useful to prevent fraud and to guarantee funds such as deposits or
prolonged delivery of products and services. The only downfall of
the process is that transactions that are authorized but not captured
and settled within 24 hours or a batch is not closed, then the
transaction will downgrade and
thus cost more. This additional expense though could be trivial
compared to its intended purpose and functionality within the sales
process.
- AVS or Address Verification Service. Address
Verification Service (AVS) is the process of obtaining a check of the
cardholders address as provided during the sale with the address of
record of the cardholder as provided to the issuing banks credit card
records. There is a fee charged by the processor for this
additional service step. It is required in card-not-present (non-swipped)
transactions. In some cases, such as foreign cards, the
information to perform this will be NOT PRESENT instead of giving a
MIS-MATCH error. At that point, it becomes an individual merchants
decision to accept the card or not.
- Average Ticket Size. This is the average
amount of a credit card sale. This is necessary information when
applying for a credit card merchant account. However, since you
may not have an account yet, you may have to estimate this. You
can estimate this by taking your sales for a period and dividing it by
the number of sales for that period. However, credit card sales
will typically be higher than cash sales so the estimate you reach in
this manner will typically be low. You will need to up your
estimate using this approximation.
- Basis Points. Basis points are a way to talk
about increased rates without respect to knowing what the bottom rate
is. This is typically used to describe your rate above your
discount rate. A basis point is 1/100th of one percent. So
201 basis points is equal to 2.01%.
- Batch. The batch is the last step in a credit
card sales transaction. Typically transaction are authorized for a
days worth of sales. These sales are authorized and stored in a
batch, until the merchant provides the goods and services. Once
those goods and services are provided to the consumer, the merchant
batches the transaction to settle. At settlement, the transaction
are committed and the funds are captured. In all cases, a terminal
or gateway batches transactions for a set period of time even in a
auth-capture type of transaction. A gateway or terminal can be set
to "manually" batch or to "automatically" batch. We suggest that
in virtually all cases, you should have this set to automatically batch.
If you manually batch, then you are responsible at the end of the day to
commit the batch and commit those transaction by submitting the batch.
Failure to do so, could result in a downgrade of all transactions in the
batch. With auto settlement, the batch is automatically closed and
submitted at the end of a set time interval without the merchants
additional involvement preventing this from happening. Between the
point of authorization and settlement, a transaction may be voided.
- Business Type. Generally Visa and MasterCard
has statistically viewed different industries and methods of processes
to determine the risks of each type of business and each way of
processing a credit card. Using these profiles, they establish
certain rates for which merchant businesses are profiled. When
applying for a merchant account, a merchant service provided needs to
know your business type and method of processing to determine your risk
profile. For example, a Retail merchant is expected to use a card
swipe terminal to transact sales. The same is true for a Wireless
merchant. Both of these types of merchants perform card-in-hand
transactions and typically have a brick and mortar business or the
customer is in front of them during the sale. A MOTO merchant is a
Mail Order Telephone Order transaction based merchant. In these
cases, the customer is not directly in front of the customer but submits
an order over US mail or over the phone. In these sorts of
transactions, a terminal would be used but the transaction would be
keyed into the terminal or into a gateway. An Internet merchant
provides sales over the Internet and typically the transaction is
entered directly by the consumer into a shopping cart that processes the
transaction via the gateway. Each of these methods of process have
their own individual rates and methods of process. This is
important, because sometimes a merchant may feel that they can simply
enter a new area of business where the risk profile is higher. For
example, a Retail merchant may feel they will take Internet sales and
key them into their terminal and thus be able to get lower fees and
rates because they are a retail customer. There is nothing further
from the truth, because the transaction will downgrade in such a
circumstance and the higher rate could be substantial than had the
merchant actually processed the card in the manner than is prescribed
for the business type. Many merchants are loosing hundreds of
dollars because of this confusion and most merchant service providers do
not discuss this. See downgrade.
- Capture. This is the step that occurs AFTER an
authorization is performed. When a capture is performed, the funds are
"captured" and a transfer is initiated to move the funds from the
cardholders account to the merchants bank account. An authorization can
be performed without a capture and this is typically called an Auth ONLY
or Authorization only transaction. AUTH CAPTURE performs the second
step of capturing the funds after the close or settlement of the batch.
The time between Authorization and Capture a merchant may perform a
VOID. A void prevents the transaction from settling and the
authorization automatically expires after a set time.
- Card-Not-Present Transactions. Transactions
where the card numbers are keyed instead of swipped into the processing
method.
- Discount Rate (Confirming Rate). The discount
rate or conforming rate is the rate that the merchant will be charged if
the transaction is processed per the type of account, in the manner
prescribed by Visa and MasterCard as well as the card issuring bank, in
conformance of all the rules and processes as prescribed and per the
type of credit card used by the consumer. It is the lowest rate
that a merchant would have to pay for the B to C use of a ordinary
consumer credit card processed in the ordinary manner prescribed by all
authorities of the transaction.
- Debit Cards. A debit card looks like a credit
card but it is not the same thing. When a consumer makes a
purchase with a debit card the transaction is immediately withdrawn from
the bank. As a result, these transactions can be less expensive to
perform by a merchant if you are in a retail card-present environment.
A credit card on the hand is billed to the consumer on a monthly basis
and the consumer may not have the funds right away to pay a transaction.
Interest fees are charged to the consumer to lend these charges to the
consumer. There is additional risk for the credit card company
that the consumer will default where as on a debit card this risk is
diminished. However, there are generally two types of debit card
transactions and this risk profile is diminished if the consumer is not
in front of the retailer. The first is Pin-Debit or Online Debit.
With Pin debit, a pinpad is provided by the merchant and the consumer
enters the pin. These type of transactions have lower risk than
the other debit card transactions. The second is signature-Debit
or Offline Debit. In these cases, no pin is collected. In a
retail transaction, a signature may be obtained. In an Internet or
MOTO transaction, no pin and no signature may be collected as well.
In such a case, the risk of a signature-less, offline debit transaction
is nearly the same as a credit card.
- Decline. A decline is the opposite of an
authorization. It indicates the cardholders bank has rejected the
transaction. It can be because of insufficient funds but there are any
number of other reasons an issuing bank can decline a transaction. Only
a cardholder can contact their bank to determine the actual reason as
this information is held in confidence.
- Downgrade. A transaction downgrades for a
particular credit card when the transaction is processed in a manner not
determined for the card risk, merchant risk, or processing risk as
prescribed by the issuing bank or by Visa and MasterCard. When a
transaction is downgraded, additional fees are charged to offset these
risks. These risks can be anything from not obtaining an AVS to
keying in a transaction instead of swiping the card on the terminal.
See more on downgrade fees here.
Most merchant service providers do not talk about this part of the
process because keeping it vague makes them more money at a huge
disservice to you. We educate our customers.
- Issuing Bank. The issuing bank is the consumers credit card
bank. The issuing bank typically determines many of the
requirements the merchant must follow to obtain the best rate for the
credit card. As a result, the merchant does not have total control
over their rates. A corporate merchant bank may have entire
different rules than a consumer credit card issuing bank.
- Non-Qualified Rate. If a transaction is
downgrade, it will incur additional fees. A non-qualified rate is
the highest rate a merchant will be charged for use of a credit card by
a consumer. In this case, the card or method of processing the
credit card created a higher than expected risk profile and this risk of
fraud or the additional work necessary to process this transaction
causes the fees to be passed on to the merchant. You need to avoid
non-qualified transactions whenever possible. However, because of
situations and because you do not control your customers card issuring
bank, you have only limited control over these type of transactions.
- Partial Qualified Rate. If a transaction is
downgraded, it will incur additional fees. A partially-qualified
rate is typically higher than the discount rate but not as high as the
non-qualified Rate. These sort of rate may occur only in select
cases.
- Settlement: The process of sending a credit card
batch or merchants "batch" to a processing network for final processing
and payment. Fees for this process are typically called Settlement
Fees. The Settlement process occurs after authorization and capture and
a batch is typically committed after products or services are rendered
in that order. This process uses to be manual, however typically in
modern day gateway processing, batches are typically auto-settled at a
set time and end of day. This is because batches not settled within a
certain time after authorization and capture may be subject to downgrade
feels.
- Swiped Transactions. Transactions where the
credit card number is transferred to the processing method using a
magnetic stripe on the credit card which is read by the processing
method ensuring the credit card number is correct and since the card is
present, the transaction caries less fraud risk.
- Transaction Fee. This is also sometimes called an
Authorization Fee. These are fees origination at the processor and so
in all cases, a transaction fee is occurred each time any communication
of any kind occurs, whether over a telephone line, leased line, a
gateway or a terminal. This fee reimburses the processing network for
the use of their transaction processing system. It occurs in all cases,
where its a normal sale, an authorization only transaction or even a
refund.
- Void. A Voided transaction is the process of
cancelling a transaction that has been authorized but as not yet been
captured and settled. If a transaction is voided before the batch
for which this transaction is set to be submitted, the customer will
never see the charge appearing on their final account statement.
- Volume (either Monthly Volume or Yearly Volume). This
is the total amount of credit card sales in a month or in a year.
You need this information when you apply for a merchant account.
If you don't presently do credit card sales, you will need to estimate
this. If you have to estimate, its typically better to estimate
low on this amount since a higher amount could result in higher
requirements by the merchant bank. If your sales increase
dramatically, most merchant banks will increase your limits without
issue as long as your estimate was not completely unrealistically low as
to some indication of fraud.
|